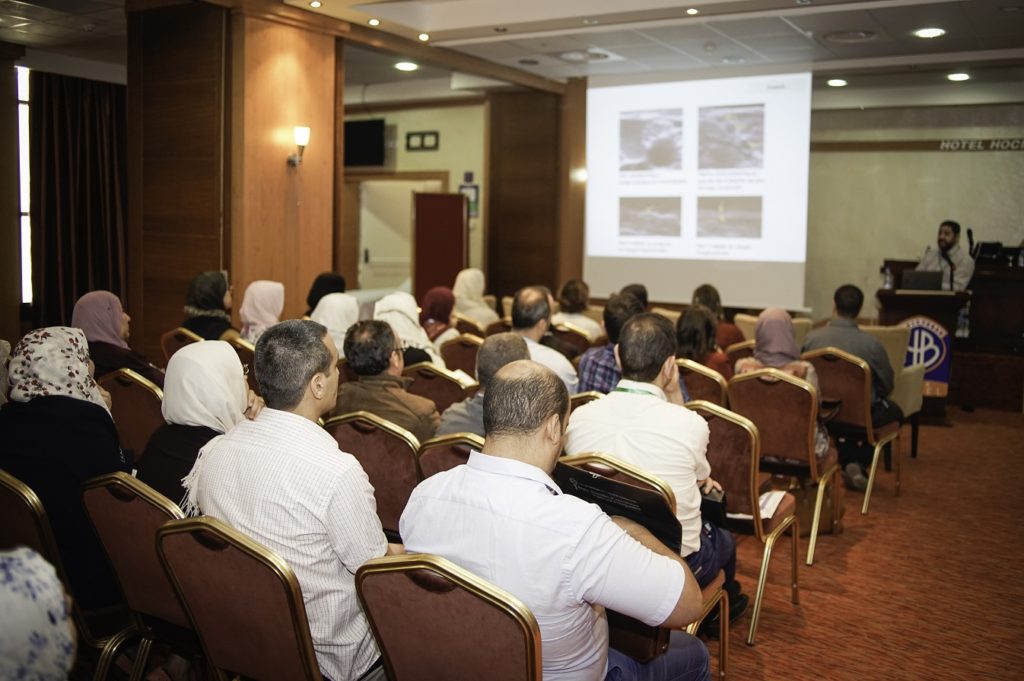
The CMAR (Club des Médecins Anesthésistes Réanimateurs) is proud to announce that in partnership with I-ALR the 2-day ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia workshop (Les premières Journées d’Anesthésie Régionale écho-guidée de Constantine) which took place 20 and 21 may 2017 in Clinique Naoufel was successful .
This 2-day ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia workshop was designed for anesthesiologists and anesthesia residents who use ultrasound in the performance of regional anesthesia.The workshop focuses on hands-on scanning and needling practice.A high level of satisfaction with the programme was demonstrated by participants.
 Dr Emmanuel Boselli Membre du bureau de i-alr Responsable du DU d’anesthésie régionale, Université Lyon I Claude Bernard
Dr Emmanuel Boselli Membre du bureau de i-alr Responsable du DU d’anesthésie régionale, Université Lyon I Claude Bernard
 Dr Ahmed Dahmane Chef de service, Centre Hospitalier Pierre Oudot, Bourgoin-Jallieu (France)
Dr Ahmed Dahmane Chef de service, Centre Hospitalier Pierre Oudot, Bourgoin-Jallieu (France)
 Dr Noreddine Bouarroudj Clinique Naoufel, Constantine Président du Club des Anesthésistes-Réanimateurs
Dr Noreddine Bouarroudj Clinique Naoufel, Constantine Président du Club des Anesthésistes-Réanimateurs
 Dr Chakib Rahmoune Hôpital Bicêtre (Hôpitaux Universitaires Paris-Sud)
Dr Chakib Rahmoune Hôpital Bicêtre (Hôpitaux Universitaires Paris-Sud)
 Dr Simahmoud Bensalem HMUS Gopital Militaire Bouchaoui Alger
Dr Simahmoud Bensalem HMUS Gopital Militaire Bouchaoui Alger
Day 1
- hands-on scanning on live models
- Opportunity to use a variety of ultrasound machines (Aloka ,Sonosite, Sonoscape, Toshiba, and ECM)
- Theoretical presentations
- Practical tips and tricks for ultrasound guided blocks
- Live scan on live models
- Hands-on scanning and needling practice on animal models with instructor feedback
- A fully interactive program
 Day 2Clinical examples (in patients) of the most used peripheral nerve block procedures:TAP blocks,Axillary Blocks,Interscalene Block,Ilioinguinal and ilio hypogastric blocks,Femoral nerve Block,Sciatic nerve bloc
Day 2Clinical examples (in patients) of the most used peripheral nerve block procedures:TAP blocks,Axillary Blocks,Interscalene Block,Ilioinguinal and ilio hypogastric blocks,Femoral nerve Block,Sciatic nerve bloc
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
ULTRASOUND PRINCIPLES
- Understand basic ultrasound physics
- Sound wave generation
- Recognize the characteristic ultrasound appearance of:
- Bone
- Fascia
- Fat
- Vessels
- Muscle
- Nerve
- Understand the factors affecting sound waves in tissues
- Understand how color Doppler can be used
ULTRASOUND MACHINE CONTROLS
- Probe selection
- Frequency filtering
- Depth adjustment
- Gain adjustment
- Time gain compensation
- Focal zone adjustment
- Color Doppler
- Preset selection
ULTRASOUND PROBE HANDLING
- Understand basic ultrasound probe
manipulations to acquire a target and optimize the image- Setup: Probe, depth, settings and approach
- Probe placement and pressure
- Anatomy recognition
- Tilt and rotation
ULTRASOUND PROBE AND NEEDLE GUIDANCE
- Learn how to orient the probe to the needle in-plane and out-of-plane
- Learn how to perform an in-plane approach
- Understand how to recognize common errors while advancing the needle and how to correct them
- Needle entry point is off-plane
- Good tissue movement but needle is not visualized
- Needle crosses ultrasound beam
- Learn how to perform an out-of-plane approach
AXILLARY NERVE BLOCK
- The muscles that border the axilla, anatomical boundaries and the surface landmarks of the axilla
- The anatomy of the terminal nerves of the brachial plexus, including their sensory and motor function
- Be able to identify the sonographic appearance of the axillary artery, axillary vein coracobrachialis, conjoined tendon of the teres major and teres minor, the short and long heads of the biceps and the triceps
- Be able to identify the median, radial and ulnar nerves
- Be able to identify the musculocutaneous nerve
- Be able to trace the nerves to confirm their identity
FEMORAL NERVE BLOCK
- dentify the nerve roots that comprise
the femoral nerve - Review the anatomy of the femoral nerve
- Review the anatomy of the femoral cutaneous nerve
- Review the anatomic course of the iliopsoas muscles
- Understand the fascial planes surrounding the femoral nerve
- Identify the key anatomic relationships of the femoral nerve to the vessels
- Review the branches of the femoral artery
- Understand the sonographic appearance of the fascial planes, femoral nerve, iliopsoas muscle and femoral vessels
SCIATIC NERVE BLOCK
- dentify the nerve roots that comprise the sciatic nerve
- Review the anatomy of the sciatic nerve
- Review the anatomy of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh
- Review the cutaneous distribution of the saphenous nerve
- Review the anatomic course of the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles
- Understand the key anatomic relationships of the sciatic nerve
- Understand the sonographic appearance of the sciatic nerve
BRACHIAL PLEXUS BLOCK
- Review the anatomy, cross-sectional anatomy
and sonoanatomy of the neck. - Identify key anatomic relationships of the brachial
plexus and surrounding structures. - Understand and master the sonographic landmark approach to the brachial plexus.
- Review approaches to identifying the brachial plexus with ultrasound.
TAP BLOCK
- Layers of the Abdominal Wall
- Innervation of the Abdominal Wall
- Sonoanatomy of the Medial Abdominal Wall and Rectus Sheath and Subcostal Region
- Mid-axillary and Posterior Approaches
ADDUCTOR CANAL BLOCK
- Differentiate Femoral and SaphenousNerve Innervation
- Understand the Anatomy of the Muscles of the Anterior Thigh
- Understand the Borders and Content of the Femoral Triangle
- Understand the Structures that Border and Define the Adductor Canal
- Understand the Contents of the Adductor Canal
- Understand the Cross-sectional Anatomy: Muscles of the Anterior Thigh
- Identify the Femoral Artery, Femoral Vein, SartoriusMuscle, Saphenous Nerve and Adductor Canal with Ultrasound
- Understand the Cross-sectional Anatomy of the mid-to-Distal Adductor Canal
- Understand the Sonoanatomyof the Distal Adductor Canal
- Understand the Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Potential Locations for Adductor Canal Blocks.
 Médecin Anesthésiste Réanimateur Algérie Constantine Dr Bouarroudj Noreddine
Médecin Anesthésiste Réanimateur Algérie Constantine Dr Bouarroudj Noreddine